Step 1: Understand Who Does What
Before diving in, it’s essential to know the difference between psychiatrists and therapists:
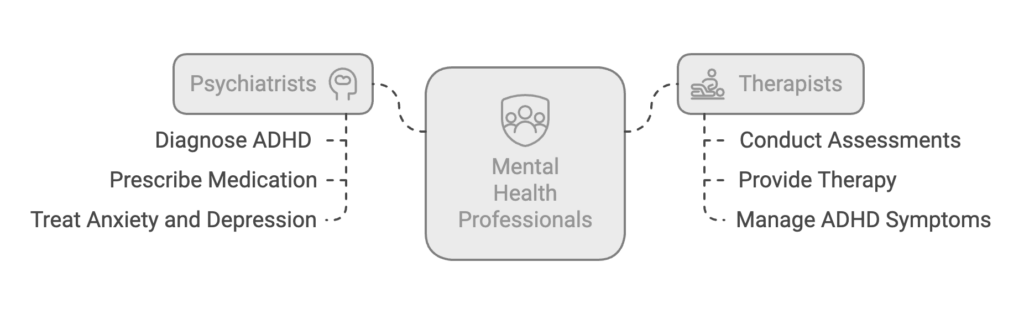
Psychiatrists
- Who They Are: Medical doctors who specialize in mental health.
- What They Do: Diagnose ADHD and can prescribe medication.
- Why See Them: If you think medication might be part of your treatment plan or if you have other mental health conditions, like anxiety or depression, alongside ADHD.
Therapists
- Who They Are: Licensed counselors, psychologists, or social workers trained in mental health.
- What They Do: Conduct assessments, provide therapy, and sometimes diagnose ADHD.
- Why See Them: If you want help managing ADHD symptoms through behavioral strategies, therapy, or support.
Step 2: Decide Where to Start
When it comes to diagnosing ADHD, there’s no “one right door.” The choice between a psychiatrist or therapist often depends on your specific needs and goals.
Start with a Psychiatrist If:
- You’re considering medication as part of your treatment.
- You suspect you might have multiple mental health conditions (like depression or anxiety) that need professional evaluation. Further on the subject: “How to Treat ADHD in Adults Without Meds,” “Do I Have ADHD or Am I Just Lazy?“.
Start with a Therapist If:
- You’re unsure whether your symptoms are ADHD or something else.
- You want to explore non-medication strategies to manage ADHD symptoms.
Pro Tip: Many people start with a therapist for initial evaluations and then get referred to a psychiatrist if medication is needed.
Step 3: What to Expect During an ADHD Diagnosis
Whether you see a psychiatrist or a therapist, here’s what the process generally looks like:
1. Initial Assessment
- Be prepared to discuss your symptoms in detail. Think about how they impact your daily life, work, or relationships.
- Common questions include:
- Do you struggle with focus, organization, or completing tasks?
- Have you experienced these symptoms since childhood?
- Are there times when you feel hyper-focused or overly impulsive?
2. Background Check (Not the FBI Kind!)
- Your provider might ask about your medical history, family history of ADHD, and any past mental health diagnoses.
- They may also request input from family members, teachers, or colleagues who’ve observed your behavior.
3. Diagnostic Tools
- Therapists and psychiatrists often use ADHD-specific tests or questionnaires, like the Conners’ Rating Scales or the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS).
- They’ll assess whether your symptoms meet the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5 (a fancy book psychiatrists use to diagnose mental health conditions).
Step 4: Be Honest About Your Symptoms
Honesty is the golden rule during an ADHD evaluation. Don’t downplay or exaggerate your symptoms—just lay it all out there. Remember, there’s no judgment here.
Step 5: Understand the Diagnosis
If your provider confirms you have ADHD, congratulations—you’re not lazy or unfocused; you’ve got a brain that’s wired differently. A diagnosis is the first step toward finding strategies and treatments that work for you.
If It’s Not ADHD:
Sometimes, other conditions (like anxiety, depression, or even sleep disorders) can mimic ADHD symptoms. Your provider will help you explore alternative explanations and treatment options if that’s the case.
Step 6: Plan Your Next Steps
Once you have a diagnosis, your provider will work with you to create a plan. Here’s what that might include:
If You See a Psychiatrist:
- Discuss medication options like stimulants (Adderall, Ritalin) or non-stimulants (Strattera).
- Set up regular check-ins to monitor how the medication is working and adjust dosages if needed.
If You See a Therapist:
- Work on coping strategies, like improving time management or building routines.
- Explore Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which can help reframe negative thought patterns and improve focus.
Step 7: Build a Support Network
ADHD is a team sport, so don’t go it alone. Share your diagnosis with trusted friends, family, or coworkers who can support you.
Final Thoughts
Getting an ADHD diagnosis isn’t about labeling yourself—it’s about understanding yourself better. Whether you start with a psychiatrist or therapist, you’re taking a proactive step toward managing your symptoms and thriving in your unique way.